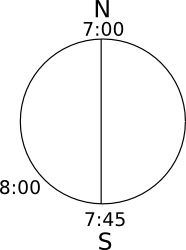
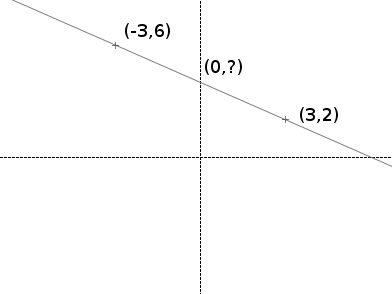
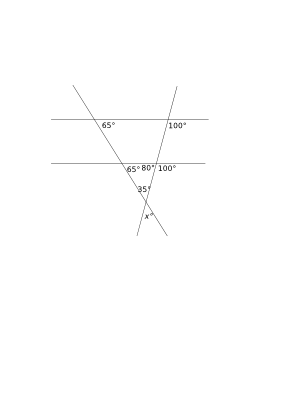
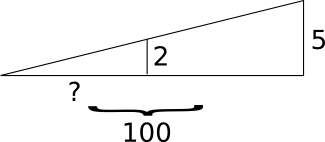
- List all of the numbers between 30 and 50:
30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
- Cross out all of the numbers divisible by 2:
30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
- Cross out all of the numbers divisible by 3:
30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
- Cross out all of the numbers divisible by 5 (we don't need to worry about numbers divisible by 4, since they are also divisible by 2):
30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
- Cross out all of the numbers divisible by 7:
30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
- We only have to check numbers less than √50, so we're done. The remaining numbers are 31, 37, 41, 43, 47. Therefore, the answer is G. 5.